Perturbing the Mitochondrial Kinase Network Mitochondria consist of Biology Diagrams Decades ago, scientists discovered cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), proteins that act as master regulators of the cell cycle. As their name indicates, the activity of CDKs is controlled by cyclins The composition of m-Cdk involves cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and their regulatory partners, cyclins. Central to this complex is the Cdk1 enzyme, which, when bound to cyclin B, forms the active m-Cdk complex. This binding dictates the kinase's activity and ensures that m-Cdk activity is precisely timed to the cell cycle's needs. The activity level of Polo kinases peaks during M phase, and they are degraded by the proteasome after exit from mitosis. The most prominent mitotic kinase is the cyclin-dependent kinase 1

The CPC is itself stabilized at chromosomes by Borealin, ensuring the continued activity of Aurora B kinase and the efficient recruitment of condensins. 18 When Borealin is knocked-out by RNA interference, mitotic progression is delayed and the consequence is "kinetochore-spindle misattachments and an increase in bipolar spindles associated

Nested Irreducible Complexity Biology Diagrams
The most prominent mitotic kinase is the cyclin-dependent kinase 1 ( Cdk1),the founding member of the activity of Cdk2,in association with either cyclin A or cyclin E 1-3.Another kinase,

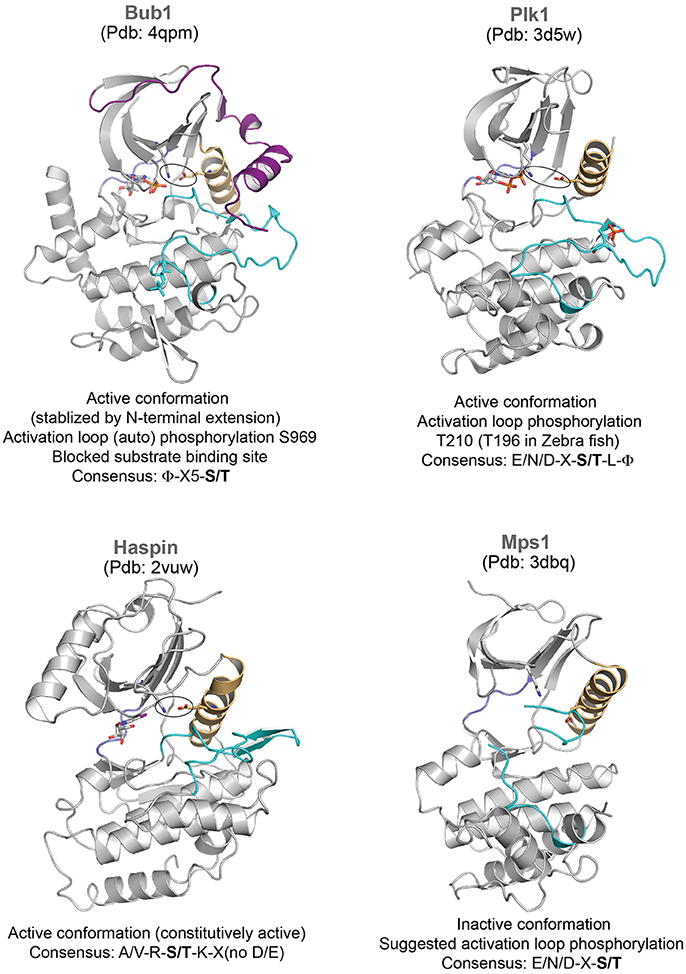
Looking at mitotic kinases from a structural perspective, it becomes apparent that kinase activation is not a binary process (from inactive to active), but that there are intermediate states that may exhibit varying degrees of activity . We will refer to these as either 'inactive' or 'partially active' states, because it is difficult to
PDF MITOTIC KINASES AS REGULATORS OF CELL DIVISION AND ITS CHECKPOINTS Biology Diagrams
Isolating the mitotic kinase activity of a promiscuous kinase. (a): CK1α is a Ser/Thr protein kinase involved in many diverse cellular processes. (b): Selective recruitment of CK1α to spindle microtubules by FAM83D: In interphase, the FAM83D-HMMR complex cannot associate with CK1α. Many mitotic kinases rely on spatial targeting to phosphorylate their specific substrates. This restricts the activity of the kinase to generate gradients of kinase activity. The most well characterized spatially-targeted kinases are Aurora A and B kinases and they appear to share the same substrate specificity (Fu et al., 2009). However Aurora
